How a Periodontist Approaches Bleeding Gum Treatment
While gums may occasionally bleed after vigorous brushing or restarting flossing, persistent bleeding often signals gum disease or another underlying condition. In these cases, bleeding gum treatment may be necessary. A periodontist will take a careful, methodical approach not only to stop the bleeding but also to promote long-term oral and gum health.
Why gums bleed
Gum bleeding often begins with plaque accumulation along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that irritates and inflames gum tissue. If not removed through consistent brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, a calcified substance that can only be scaled off the teeth. As tartar builds up, the gums become swollen, tender, and more likely to bleed. This is known as gingivitis (early-stage gum disease). Fortunately, it is reversible with bleeding gum treatment.
Other factors can cause gums to bleed. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, certain medications, vitamin deficiencies, and health conditions like diabetes can all increase gum sensitivity. Smoking and poor nutrition further slow the body’s ability to heal and resist infection. Professional evaluation is the most effective way to identify the cause of gum bleeding and recommend the right treatment.
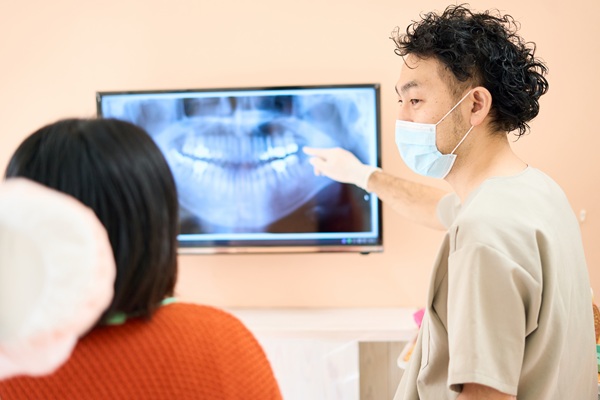
The periodontal evaluation before bleeding gum treatment
When a patient visits a periodontist for bleeding gum treatment, the process begins with a detailed periodontal evaluation. This examination allows them to measure the health of both soft and hard tissues and detect signs of early or advanced disease. They will measure pocket depth between the gums and teeth, assessing how firmly the tissue attaches to the roots. Digital imaging or X-rays also show whether bone loss has occurred beneath the surface, while a visual assessment identifies areas of inflammation, tartar buildup, or gum recession.
With these findings, the periodontist can determine the stage of gum disease and design a customized plan that addresses the cause rather than just the symptoms. This personalized approach ensures that treatment targets bacteria, strengthens tissue, and helps prevent recurrence.
Non-surgical bleeding gum treatment
Early gum disease is often treatable without surgery. The most common approach is scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar buildup from beneath the gums. The scaling step eliminates bacterial buildup, while root planing smooths the surfaces of the tooth roots to make it harder for bacteria to reattach. Through this procedure, a periodontist helps the gums heal and reattach firmly to the teeth.
The periodontist may also prescribe antibacterial rinses or topical treatments to reduce inflammation and infection further. They will guide patients on how to practice better gum care at home, such as careful flossing and gentle brushing. Then, regular follow-up visits help track healing and prevent the problem from returning or worsening.
Advanced procedures for bleeding gums
When bleeding gums are caused by more advanced periodontitis, deeper intervention is often necessary to repair damage and protect long-term oral health. In these cases, the periodontist may recommend procedures that eliminate infection and regenerate lost bone or tissue. For example, flap surgery lifts the gums, removes tartar from deeper areas, and repositions the tissue securely around the teeth. Another common example is bone grafting or gum grafting, which can help rebuild areas of the mouth weakened by gum disease.
Why choose a periodontist for bleeding gum treatment?
A periodontist’s role extends beyond treating immediate symptoms, like bleeding gums. The focus is on restoring complete gum health and reinforcing the foundation that supports every tooth. Regular periodontal maintenance appointments help detect recurring inflammation early and ensure the gums remain strong. The periodontist also educates patients about systemic connections, such as the link between gum disease and diabetes, empowering them to take control of both oral and general health.
How to prevent future gum bleeding
Successful bleeding gum treatment relies on ongoing prevention. Even after professional treatment, maintaining healthy gums requires consistent daily habits and regular follow-up care. Periodontists emphasize prevention as a shared responsibility between the patient and the dental team. To maintain gum health and prevent bleeding, patients should:
- Brush twice daily with a soft toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss gently each day to remove plaque between teeth and along the gumline.
- Use an antibacterial mouth rinse to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Visit a dental provider regularly for cleanings and monitoring.
- Avoid tobacco, which can delay healing and worsen gum disease.
These simple steps, when performed consistently, greatly reduce the risk of gum disease recurrence and protect both gum and bone health.
Contact our Cypress team today
Healthy gums are essential to every confident smile. Through professional treatments and ongoing preventive care, our team works to stop bleeding, reverse damage, and create a stable foundation for the teeth. Contact Charles E. Dyer IV, DDS, MS, PC to learn more about bleeding gum treatment.
Request an appointment here: https://www.charlesdyeriv.com or call Charles E. Dyer IV, DDS, MS, PC at (281) 213-0900 for an appointment in our Cypress office.
Check out what others are saying about our dental services on Yelp: Bleeding Gum Treatment in Cypress, TX.
Related Posts
Understanding what causes bleeding gums is vital for preventing this common condition and promoting proper oral hygiene. Dentists can make recommendations to help patients maintain healthy gums and avoid widespread health and oral complications.People frequently dismiss gum bleeding as a normal consequence of overly aggressive brushing or flossing. Using a toothbrush with stiff bristles might…
In and of themselves, bleeding gums are not a huge cause for concern. However, the cause is worth investigating, as it may indicate a serious condition, such as gum disease or gingivitis, or the root of the issue may be nothing more than a change in dental hygiene habits. Before you panic, check out these…
You are not alone if you experience bleeding gums when brushing your teeth. You might not realize that bleeding gums are not normal and are a sign of gingivitis. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease. The gums may become inflamed and appear brighter red. Improper brushing and flossing can irritate your gums further…
Bleeding gums are a hallmark sign of gingivitis. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease. Inflammation in your gums can cause them to appear red and puffy. Your gums may bleed when you brush or floss your teeth the way you normally do. You may have healthy gums and still develop gingivitis during pregnancy.…
